Photonchina’s wollaston polarizer can separate an incident beam into two rays: extraordinary and ordinary ray with a deviation angle which is dependent on wavelength. Both rays are transmitted through the other surface.
What is Wollaston Polarizer?
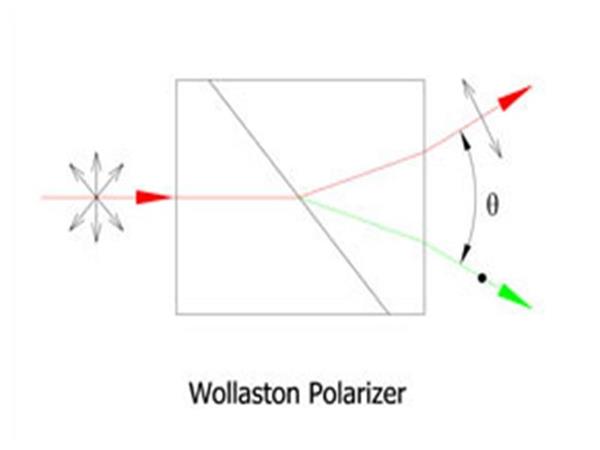
Wollaston polarizer or Wollaston prism is an optical element separating two orthogonally polarized beams. The difference between BD crystal and Wollaston prism is that the former separates two beams by a lateral distance, while the latter separates two beams by an angle.
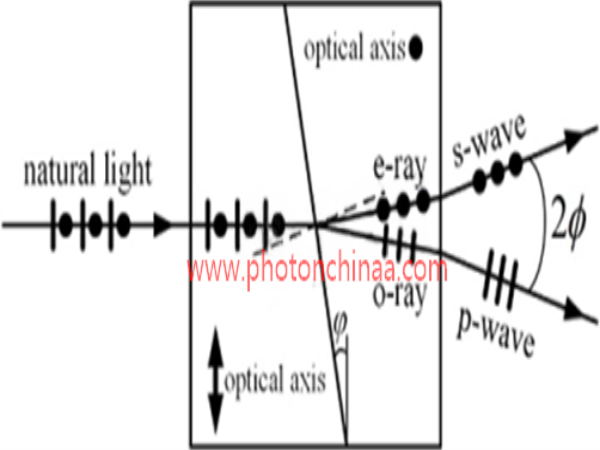
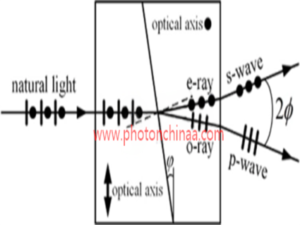
As shown in the following illustration, a Wollaston polarizer comprises two wedges made of uniaxial crystal. The optical axes of the wedges are both parallel to the right angle surfaces, while the two optical axes are perpendicular to each other when the wedges are assembled together. Thus in the first and second wedges, the p-wave acts first as e-ray and then as o-ray, while the s-wave acts as first o-ray and then e-ray.
Illustration: Separation of two orthogonally polarized beams in a Wollaston Prism
How does a Wollaston Polarizer work?
From above drawing, we may see the natural light incidents on the first wedge normally. O-ray and e-ray keeps coincidence in the first wedge but transmit in different speed (c/no and c/ne, given c as the optical velocity in vacuum). When the two rays are refracted at the angular surface between two wedges, the refraction angles are different. One is larger than the incident angle φ and the ray turns downward. The other is smaller than φ and the ray turns upward. The angular deviation between the two rays is enlarged after refraction at the right angular surface of the second wedge. Based on paraxial approximation, the final deviation angle between the separated s-wave and p-wave is given by Euaqtion below.
Wollaston prism is widely used in optical devices such as optical isolator, polarization beam combiner/splitter, optical circulator, and wavelength selective switch, etc.
Specifications of Wollaston Polarizer of Photonchina:
| Material: | a-BBO, Calcite ,YVO4,Quartz |
| Wavelength Range: | a-BBO:190-3500 nm, Calcite:350-2300 nm, YVO4:400-5000 nm,Quartz:200-2300 nm |
| Extinction Ratio: | Calcite,Quartz:<5×10-5; a-BBO,YVO4:<5×10-6 |
| Parallelism: | <1 arc Min |
| Surface Quality: | 20/10 |
| Beam Deviation: | < 3 arc minutes |
| Wavefornt Distortion: | λ/4@632.8nm |
| Damage Threshold: | >500 MW/cm2 |
| Coating: | Single MgF2 |
| Mount: | Black Anodized Aluminium |
-
a-BBO Wollaston Polarizer
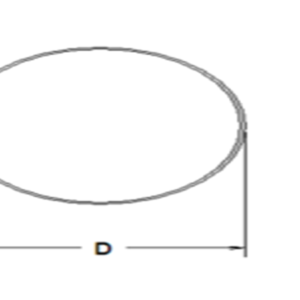
| Wavelength Range | Extinction Ratio | Separation Angle | C.A.φa (mm) | O.D.φd (mm) | L (mm) |
| 190~3500nm | <5×10-6 | 16° @800nm | 6.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 |
| 8.0 | 25.4 | 17.0 | |||
| 10.0 | 25.4 | 19.0 | |||
| 15.0 | 30.0 | 23.0 |
-
Calcite Wollaston Polarizer
| Wavelength Range | Extinction Ratio | Separation Angle | C.A.φa (mm) | O.D.φd (mm) | L (mm) |
| 350~2300nm | <5×10-5 | 19° @980nm | 6.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 |
| 8.0 | 25.4 | 17.0 | |||
| 10.0 | 25.4 | 19.0 | |||
| 15.0 | 30.0 | 23.0 | |||
| 20.0 | 38.0 | 29.0 |
-
Yvo4 Wollaston Polarizer
| Wavelength Range | Extinction Ratio | Separation Angle | C.A.φa (mm) | O.D.φd (mm) | L (mm) |
| 400~4000nm | <5×10-6 | 20° @1550nm | 6.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 |
| 8.0 | 25.4 | 17.0 | |||
| 10.0 | 25.4 | 19.0 | |||
| 15.0 | 30.0 | 23.0 | |||
| 20.0 | 38.0 | 29.0 |
-
Quartz Wollaston Polarizer
| Wavelength Range | Extinction Ratio | Separation Angle | C.A.φa (mm) | O.D.φd (mm) | L (mm) |
| 200~2300nm | <5×10-4 | 2° @1064nm | 6.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 |
| 8.0 | 25.4 | 24.0 | |||
| 10.0 | 25.4 | 28.0 | |||
| 15.0 | 30.0 | 38.0 | |||
| 20.0 | 38.0 | 48.0 |